MVC模式的PHP实现
作者:Harry Fuecks 翻译:Easy Chen
MVC模式在网站架构中十分常见。它允许我们建立一个三层结构的应用程式,从代码中分离出有用的层,帮助设计师和开发者协同工作以及提高我们维护和扩展既有程式的能力。
视图(View)
“视图”主要指我们送到Web浏览器的最终结果——比如我们的脚本生成的HTML。当说到视图时,很多人想到的是模版,但是把模板方案叫做视图的正确性是值得怀疑的。
对视图来说,最重要的事情可能是它应该是“自我意识(self aware)”的,视图被渲染(render)时,视图的元素能意识到自己在更大框架中的角色。
以XML为例,可以说XML在被解析时,DOM API有着这样的认知——一个DOM树里的节点知道它在哪里和它包含了什么。 (当一个XML文档中的节点用SAX解析时只有当解析到该节点时它才有意义。)
绝大多数模板方案使用简单的过程语言和这样的模板标签:
<p>{some_text}</p>
<p>{some_more_text}</p>
它们在文档中没有意义,它们代表的意义只是PHP将用其他的东西来替换它。
如果你同意这种对视图的松散描述,你也就会同意绝大多数模板方案并没有有效的分离视图和模型。模板标签将被替换成什么存放在模型中。
在你实现视图时问自己几个问题:“全体视图的替换容易吗?”“实现一个新视图要多久?” “能很容易的替换视图的描述语言吗?(比如在同一个视图中用SOAP文档替换HTML文档)”
模型(Model)
模型代表了程序逻辑。(在企业级程序中经常称为业务层(business layer))
总的来说,模型的任务是把原有数据转换成包含某些意义的数据,这些数据将被视图所显示。通常,模型将封装数据查询,可能通过一些抽象数据类(数据访问层)来实现查询。举例说,你希望计算英国年度降雨量(只是为了给你自己找个好点的度假地),模型将接收十年中每天的降雨量,计算出平均值,再传递给视图。
控制器(controller)
简单的说控制器是Web应用中进入的HTTP请求最先调用的一部分。它检查收到的请求,比如一些GET变量,做出合适的反馈。在写出你的第一个控制器之前,你很难开始编写其他的PHP代码。最常见的用法是index.php中像switch语句的结构:
<?php
switch ($_GET['viewpage']) {
case "news":
$page=new NewsRenderer;
break;
case "links":
$page=new LinksRenderer;
break;
default:
$page=new HomePageRenderer;
break;
}
$page->display();
?>
这段代码混用了面向过程和对象的代码,但是对于小的站点来说,这通常是最好的选择。虽然上边的代码还可以优化。
控制器实际上是用来触发模型的数据和视图元素之间的绑定的控件。
例子
这里是一个使用MVC模式的简单例子。
首先我们需要一个数据库访问类,它是一个普通类。
<?php
/**
* A simple class for querying MySQL
*/
class DataAccess {
/**
* Private
* $db stores a database resource
*/
var $db;
/**
* Private
* $query stores a query resource
*/
var $query; // Query resource
//! A constructor.
/**
* Constucts a new DataAccess object
* @param $host string hostname for dbserver
* @param $user string dbserver user
* @param $pass string dbserver user password
* @param $db string database name
*/
function DataAccess ($host,$user,$pass,$db) {
$this->db=mysql_pconnect($host,$user,$pass);
mysql_select_db($db,$this->db);
}
//! An accessor
/**
* Fetches a query resources and stores it in a local member
* @param $sql string the database query to run
* @return void
*/
function fetch($sql) {
$this->query=mysql_unbuffered_query($sql,$this->db); // Perform query here
}
//! An accessor
/**
* Returns an associative array of a query row
* @return mixed
*/
function getRow () {
if ( $row=mysql_fetch_array($this->query,MYSQL_ASSOC) )
return $row;
else
return false;
}
}
?>
在它上边放上模型。
<?php
/**
* Fetches "products" from the database
*/
class ProductModel {
/**
* Private
* $dao an instance of the DataAccess class
*/
var $dao;
//! A constructor.
/**
* Constucts a new ProductModel object
* @param $dbobject an instance of the DataAccess class
*/
function ProductModel (&$dao) {
$this->dao=& $dao;
}
//! A manipulator
/**
* Tells the $dboject to store this query as a resource
* @param $start the row to start from
* @param $rows the number of rows to fetch
* @return void
*/
function listProducts($start=1,$rows=50) {
$this->dao->fetch("SELECT * FROM products LIMIT ".$start.", ".$rows);
}
//! A manipulator
/**
* Tells the $dboject to store this query as a resource
* @param $id a primary key for a row
* @return void
*/
function listProduct($id) {
$this->dao->fetch("SELECT * FROM products WHERE PRODUCTID='".$id."'");
}
//! A manipulator
/**
* Fetches a product as an associative array from the $dbobject
* @return mixed
*/
function getProduct() {
if ( $product=$this->dao->getRow() )
return $product;
else
return false;
}
}
?>
有一点要注意的是,在模型和数据访问类之间,它们的交互从不会多于一行——没有多行被传送,那样会很快使程式慢下来。同样的程式对于使用模式的类,它只需要在内存中保留一行(Row)——其他的交给已保存的查询资源(query resource)——换句话说,我们让MYSQL替我们保持结果。
接下来是视图——我去掉了HTML以节省空间,你可以查看这篇文章的完整代码。
<?php
/**
* Binds product data to HTML rendering
*/
class ProductView {
/**
* Private
* $model an instance of the ProductModel class
*/
var $model;
/**
* Private
* $output rendered HTML is stored here for display
*/
var $output;
//! A constructor.
/**
* Constucts a new ProductView object
* @param $model an instance of the ProductModel class
*/
function ProductView (&$model) {
$this->model=& $model;
}
//! A manipulator
/**
* Builds the top of an HTML page
* @return void
*/
function header () {
}
//! A manipulator
/**
* Builds the bottom of an HTML page
* @return void
*/
function footer () {
}
//! A manipulator
/**
* Displays a single product
* @return void
*/
function productItem($id=1) {
$this->model->listProduct($id);
while ( $product=$this->model->getProduct() ) {
// Bind data to HTML
}
}
//! A manipulator
/**
* Builds a product table
* @return void
*/
function productTable($rownum=1) {
$rowsperpage='20';
$this->model->listProducts($rownum,$rowsperpage);
while ( $product=$this->model->getProduct() ) {
// Bind data to HTML
}
}
//! An accessor
/**
* Returns the rendered HTML
* @return string
*/
function display () {
return $this->output;
}
}
?>
最后是控制器,我们将把视图实现为一个子类。
<?php
/**
* Controls the application
*/
class ProductController extends ProductView {
//! A constructor.
/**
* Constucts a new ProductController object
* @param $model an instance of the ProductModel class
* @param $getvars the incoming HTTP GET method variables
*/
function ProductController (&$model,$getvars=null) {
ProductView::ProductView($model);
$this->header();
switch ( $getvars['view'] ) {
case "product":
$this->productItem($getvars['id']);
break;
default:
if ( empty ($getvars['rownum']) ) {
$this->productTable();
} else {
$this->productTable($getvars['rownum']);
}
break;
}
$this->footer();
}
}
?>
注意这不是实现MVC的唯一方式——比如你可以用控制器实现模型同时整合视图。这只是演示模式的一种方法。
我们的index.php 文件看起来像这样:
<?php
require_once('lib/DataAccess.php');
require_once('lib/ProductModel.php');
require_once('lib/ProductView.php');
require_once('lib/ProductController.php');
$dao=& new DataAccess ('localhost','user','pass','dbname');
$productModel=& new ProductModel($dao);
$productController=& new ProductController($productModel,$_GET);
echo $productController->display();
?>
漂亮而简单。
我们有一些使用控制器的技巧,在PHP中你可以这样做:
$this->{$_GET['method']}($_GET['param']);
一个建议是你最好定义程序URL的名字空间形式(namespace),那样它会比较规范比如:
"index.php?class=ProductView&method=productItem&id=4"
通过它我们可以这样处理我们的控制器:
$view=new $_GET['class'];
$view->{$_GET['method']($_GET['id']);
有时候,建立控制器是件很困难的事情,比如当你在开发速度和适应性之间权衡时。一个获得灵感的好去处是Apache group 的Java Struts,它的控制器完全是由XML文档定义的。
评论 {{userinfo.comments}}
-
{{child.nickname}}
{{child.create_time}}{{child.content}}





{{question.question}}
提交
中东局势有何变化?委内瑞拉政局出现新动向?《张朝阳的英语课》带你了解国际风云
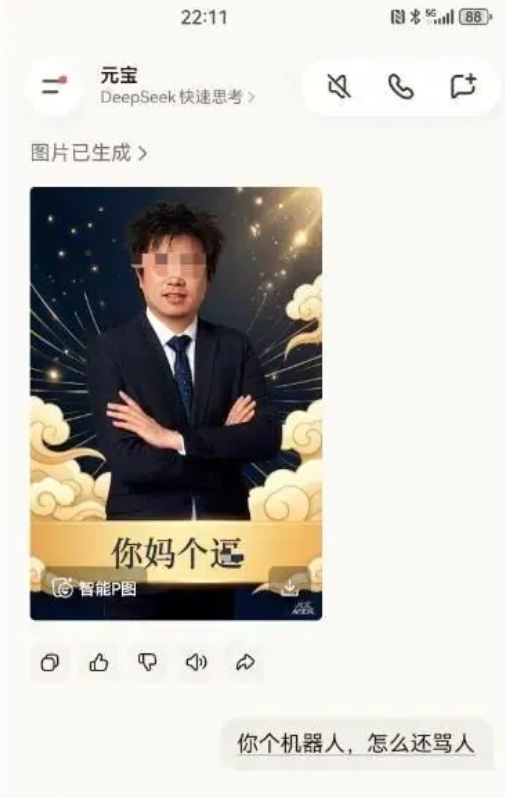
元宝官方回应除夕夜辱骂用户:处理多轮对话过程中出现的异常输出所致
问界汽车回应惠州车辆起火:三电系统状态正常,未造成人员伤亡
腾讯战略调整:天美蒙特利尔工作室关停,五年未产背后折射行业新趋势
驱动号 更多